Introduction: The Battle of Web Server Titans
In the ever-evolving landscape of web technologies, two giants have consistently dominated the web server market: Apache and Nginx. As we navigate through 2025, the choice between these powerful platforms has become increasingly nuanced, requiring a deep understanding of their capabilities, strengths, and limitations.
Historical Context and Evolution
Apache: The Veteran Web Server
Launched in 1995 by the Apache Software Foundation, Apache HTTP Server quickly became the most popular web server globally. Its open-source nature and incredible flexibility made it the go-to solution for developers and organizations of all sizes. For nearly three decades, Apache has been the backbone of countless websites, providing robust and adaptable web hosting solutions.
Nginx: The Performance Disruptor
Emerging in 2004, Nginx was created by Igor Sysoev as a revolutionary solution to the C10k problem – the challenge of handling 10,000 concurrent connections efficiently. Born out of necessity, Nginx introduced an event-driven, asynchronous architecture that challenged traditional web server paradigms.
Architectural Deep Dive
Apache’s Architectural Approach

Apache employs a process-driven architecture with a modular design that allows for extensive customization. Key characteristics include:
- Dynamic module loading
- Supports multiple programming languages
- Configurable through .htaccess files
- Highly versatile configuration options
Nginx’s Architectural Innovation
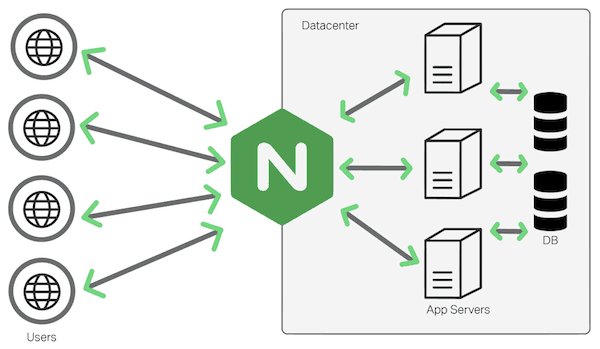
In contrast, Nginx adopts a lightweight, event-driven approach focused on core web serving capabilities:
- Asynchronous, non-blocking architecture
- Minimal resource consumption
- Superior handling of concurrent connections
- Built-in reverse proxy and load balancing
Performance Benchmarks
Performance Metrics Breakdown
| Metric | Apache | Nginx |
|---|---|---|
| Static Content Delivery | Good | Excellent |
| Dynamic Content Handling | Excellent | Good |
| Concurrent Connections | Limited | Superior |
| Memory Usage | Higher | Lower |
Real-World Performance Implications
Nginx consistently outperforms Apache in handling static content and concurrent connections. For dynamic content and complex applications, Apache maintains a competitive edge due to its flexible module system.
Use Case Scenarios
When to Choose Apache
- WordPress and PHP-heavy websites
- Shared hosting environments
- Applications requiring extensive module support
- Dynamic content-intensive platforms
- Complex configuration requirements
When to Choose Nginx
- High-traffic websites
- Microservices architectures
- Content delivery networks (CDNs)
- Reverse proxy implementations
- Performance-critical applications
Security Considerations
Apache Security Features
Apache offers comprehensive security through:
- Robust access control mechanisms
- Extensive authentication modules
- Regular security updates
- Detailed logging capabilities
Nginx Security Advantages
Nginx provides security through:
- Minimal attack surface
- Efficient request filtering
- Advanced SSL/TLS support
- Built-in protection against common vulnerabilities
Market Trends and Adoption
As of 2025, the web server market shows:
- Nginx: 34% market share
- Apache: 28% market share
- Other servers: 38% market share
Hybrid and Modern Approaches
Many organizations now implement hybrid architectures, leveraging both Apache and Nginx:
- Nginx as a reverse proxy
- Apache handling backend processing
- Optimized for specific workload requirements
Future Outlook
Emerging Trends
- Enhanced cloud-native support
- Improved containerization compatibility
- Advanced HTTP/3 implementations
- Machine learning-driven optimizations
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
There’s no universal “best” web server. Your choice depends on:
- Specific project requirements
- Expected traffic volumes
- Content delivery needs
- Performance expectations
- Technical expertise
Recommendations
- Small to medium websites: Consider Nginx
- Complex, module-dependent applications: Explore Apache
- High-traffic platforms: Investigate hybrid solutions
Final Advice
Continuously evaluate your infrastructure, stay updated with technological advancements, and be prepared to adapt your web server strategy as your project evolves.
